- Home
- The Endocannabinoid System (ECS)
The Endocannabinoid System (ECS)
WHAT IS THE ENDOCANNABINOID SYSTEM (ECS)?
Before you begin consuming CBD, you must first learn about the endocannabinoid system. The endocannabinoid system, abbreviated as ECS, is a series of receptors that are found throughout the body.
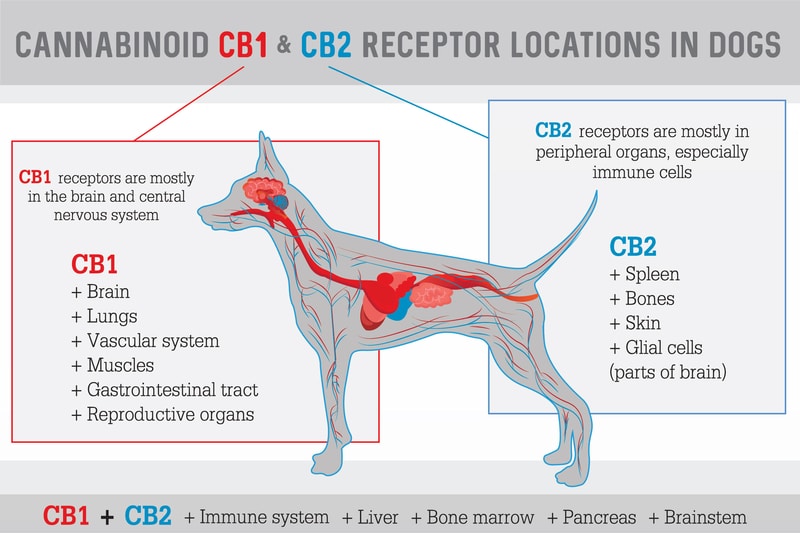
The ECS is broken into two main categories – the CB1 and CB2 groups. The CB1 receptor group is found primarily in the nerve cells of the brain, spinal cord, peripheral organs, and white blood cells; along with the urinary, reproductive, and gastrointestinal tract.
The CB2 receptor group is found primarily in the microglia of the central nervous system, along with the immune system.
In regards to CBD, the CB2 receptor group is the primary location that CBD interacts with. However, research shows that CBD does overlap between the CB1 and CB2 receptor groups; however, CBD is more prevalent among CB2 receptors.
Considering that CBD primarily affects the CB2 group, which encompasses the immune system and central nervous system – it’s no wonder why CBD is associated with a plethora of supportive qualities.

How CBD Works With The Endocannabinoid System
When you consume CBD via inhalation, ingestion or topical absorption – the CBD molecules quickly find their way via your blood to bind to CB2 receptors.
Once in contact, CBD triggers the endocannabinoid system to stimulate the central nervous system and the immune system. The results are categorized as immunoregulation and neuroprotection.[1]
By stimulating the endocannabinoid system, CBD pushes your body to modulate its immune response by increasing the development of cytokines. Cytokines are necessary proteins that regulate immune response and inflammation throughout the body.[2]
In regards to the central nervous system, CBD triggers the endocannabinoid system to increase the production of vital neurotransmitters – such as serotonin. Serotonin is a key neurotransmitter within the central nervous system, and plays a key role in the regulation of mood, sleep, pain management, and energy.
The release of serotonin assists with depression, anxiety, pain, and insomnia. Various studies show that CBD actually interacts directly with serotonin receptors, which shows the varied pathways that CBD ventures throughout your body.[3]
By interacting directly with the endocannabinoid system, CBD harnesses the body’s natural ability to support a wide variety of mental and physical issues.
Furthermore, CBD is well-known to sidestep the endocannabinoid system and interact with secondary proteins and receptors directly to promote supportive effects. Examples are TRPV1 proteins (transient receptor villanoid proteins) and PPARs (peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors).
[1] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3044336/
[2] https://bio.libretexts.org/Bookshelves/Microbiology/Book%3A_Microbiology_(Kaiser)/Unit_5%3A_Innate_Immunity/11.4%3A_Early_Induced_Innate_Immunity/11.3C%3A_Cytokines_Important_in_Innate_Immunity

























